Ohm's Law | Electricity and Magnetism
Materials have a characteristic behavior of resisting the flow of electric charge. This physical property, or ability to resist current, is known as resistance and is represented by the symbol R. The resistance of any material is directly proportional to its length(l) and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area(A). This can be represented by the mathematical formula,
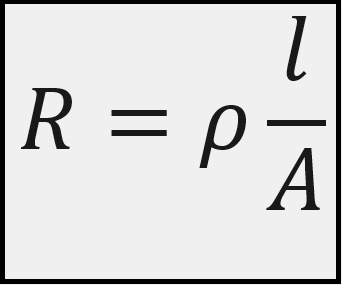
Where ρ is known as the resistivity of the material in ohm-meters. Good conductors, such as copper and aluminum, have low resistivities, while insulators, such as mica and paper, have high resistivities. The circuit element used to model the current-resisting behavior of a material is the resistor. For the purpose of constructing circuits, resistors are usually made from metallic alloys and carbon compounds.
| Resistivity of common materials. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Material | Resistivity(Ω•m) | Usage |
| Silver | 1.64x10-8 | Conductor |
| Copper | 1.72x10-8 | Conductor |
| Aluminum | 2.8x10-8 | Conductor |
| Gold | 2.45x10-8 | Conductor |
| Carbon | 4x10-5 | Semiconductor |
| Germanium | 47x10-2 | Semiconductor |
| Silicon | 6.4x102 | Semiconductor |
| Paper | 1010 | Insulator |
| Mica | 5x1011 | Insulator |
| Glass | 1012 | Insulator |
| Teflon | 3x1012 | Insulator |
The circuit component used to model the current-resisting behavior of a material is resistor. Resistors are commonly made from metallic alloys and carbon compounds. Resistors are one of the building blocks in constructing circuits. The standard notation for resistor in a circuit is R, hence the name resistor. This component is the simplest passive element
It is good to note that Sir Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist, is credited by discovering the relationship between current and voltage for a resistor. Which is now well known as the Ohm’s Law.
Ohm’s law states that the voltage (V) across a resistor is directly proportional to
the current (I) flowing through the resistor.
That is;
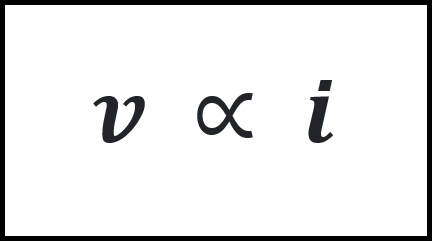
Ohm defined the constant of proportionality for a resistor to be the resistance, R( resistance is defined as a material property which can change if the internal or external conditions of the element are changed, like change in temperature). Therefore, we can mathematically represent Ohm’s Law as;
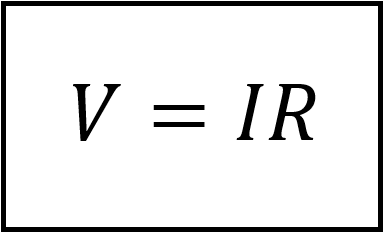
Wherein R is measured in ohms, designated as Ω. Hence, the resistance R of an element denotes its ability to resist the flow of electric current; it is measured in ohms (Ω).
We can deduce from the recent equation and get;
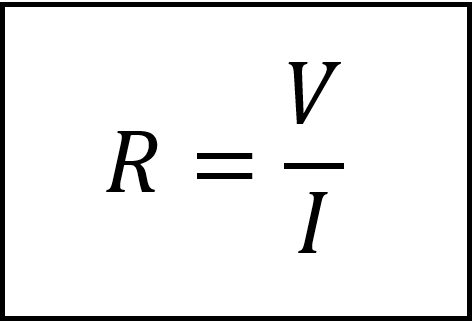
Therefore:
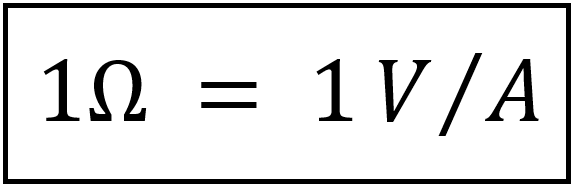
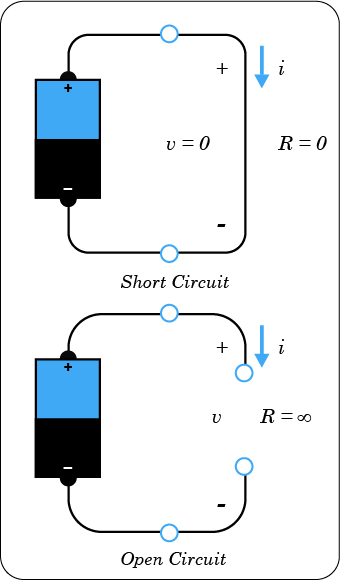
Short and Open Circuit
In order to apply Ohm’s law, we must pay attention to the current and voltage polarity. The direction of the current and the polarity of the voltage must follow the passive sign convention. This means that the current flows from a higher potential to a lower potential in order for V = IR. If the current flows from lower to a higher potential a negative sign must be added to the equation to denote that direction of the flow of the current. Hence V = -IR
Given that the value of R can range from zero to infinity, it is important that we consider the two extreme possible values of R. An element with zero value of R is called short circuit. Mathematically;
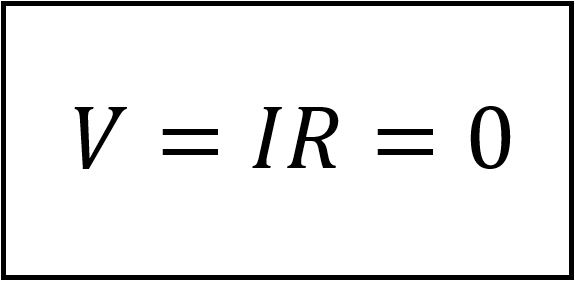
For a short circuit, showing that the voltage is zero but the current could be anything. In reality, a short circuit is usually a connecting wire assumed to be a perfect conductor (that is R=0Ω). Therefore,
A short circuit is a
circuit with resistance approaching zero.
Similarly, an element with R = ∞ is know as open circuit. We can express this as;
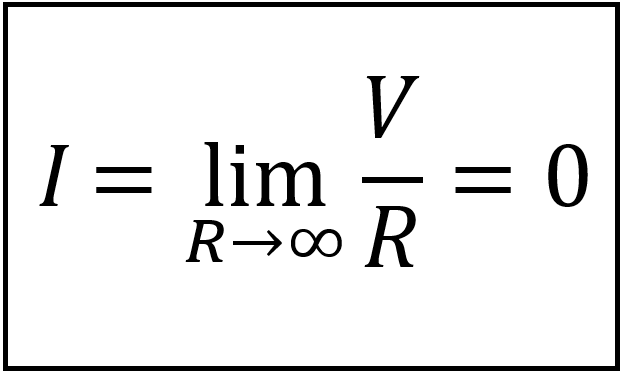
For an open circuit, indicating that the current is zero even if the voltage could be anything. Therefore,
An open circuit is a circuit element with a resistance value approaching
infinity.
Conductance
A very useful unit in circuit analysis is the reciprocal of resistance R, know as conductance and it is denoted by the letter G.
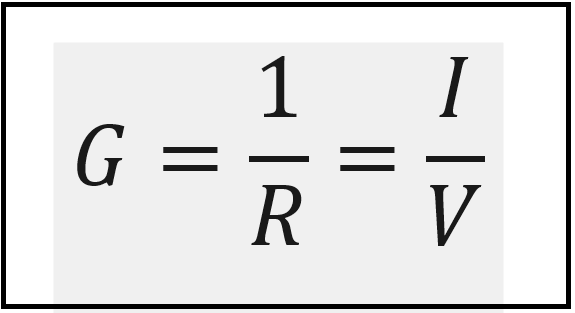
Conductance is a measure of how well am element conducts electrical current. The unit used in conductance is the mho, which is a reverse spelling of ohm, or reciprocal of ohm using the symbol ℧, which is an inverted omega symbol. Even though engineers use the mho, other books and articles use the unit siemens(S), which is the SI unit of conductance.
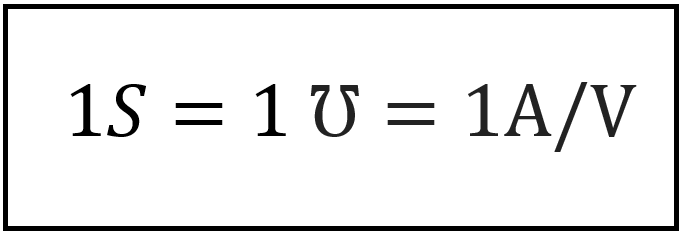
Conductance is the ability of an element to conduct electrical current; it is
measured in mhos(℧) or in siemen(S).

